Welcome to TollBit
Overview & platform documentation
Executive Summary
The AI-Publisher ecosystem lacks a standardized protocol for consent, compliance, and remuneration. TollBit provides this infrastructure layer.
- For Publishers: We provide control, safety, and monetization tools to onboard their content for the AI era.
- For AI Partners: We provide a single, compliant interface to access the agent web — whether you need real-time fetching for RAG, bulk ingestion for indexing, or specific rights-cleared datasets.
This document details the TollBit Platform, encompassing the publisher onboarding journey (Supply) and the technical integration standards (Demand).
For Publishers
Section 1: Publisher Onboarding & Identity
Objective: To demonstrate the end-to-end workflow of how a publisher, whether a niche blog or a multinational media conglomerate, activates their content for the TollBit ecosystem. This process is fully self-serve and designed to handle complex organizational hierarchies.
1.1 Account Creation & Organization Structure
The TollBit hierarchy is designed to support complex media organizations with multiple titles and regional divisions.
The Organization: The top-level entity (e.g., "Hearst Magazines"). This entity holds the billing details, tax information (W-9), and global admin users.
The Property: A specific domain or publication (e.g. "Caranddriver.com", "Esquire.com"). Settings, logs, and analytics are scoped to the Property level.
Step 1: Sign Up & Organization Setup
- User authenticates via email/SSO.
- User defines the Organization Name and Billing Country.
Step 2: Team Management (RBAC)
Admins can invite team members with specific roles:
- Admin: Full access to billing, legal, and setting license terms.
- Member: Access to analytics, content rights and setting rates.
1.2 Property Addition & Provenance
TollBit enforces strict domain ownership verification. This prevents "spoofing," ensuring that partners only interact with verified content owners.
Step 1: DNS Verification: Before a publisher can publish rates or receive transactions, they must verify ownership via a TXT record in their top-level domain.
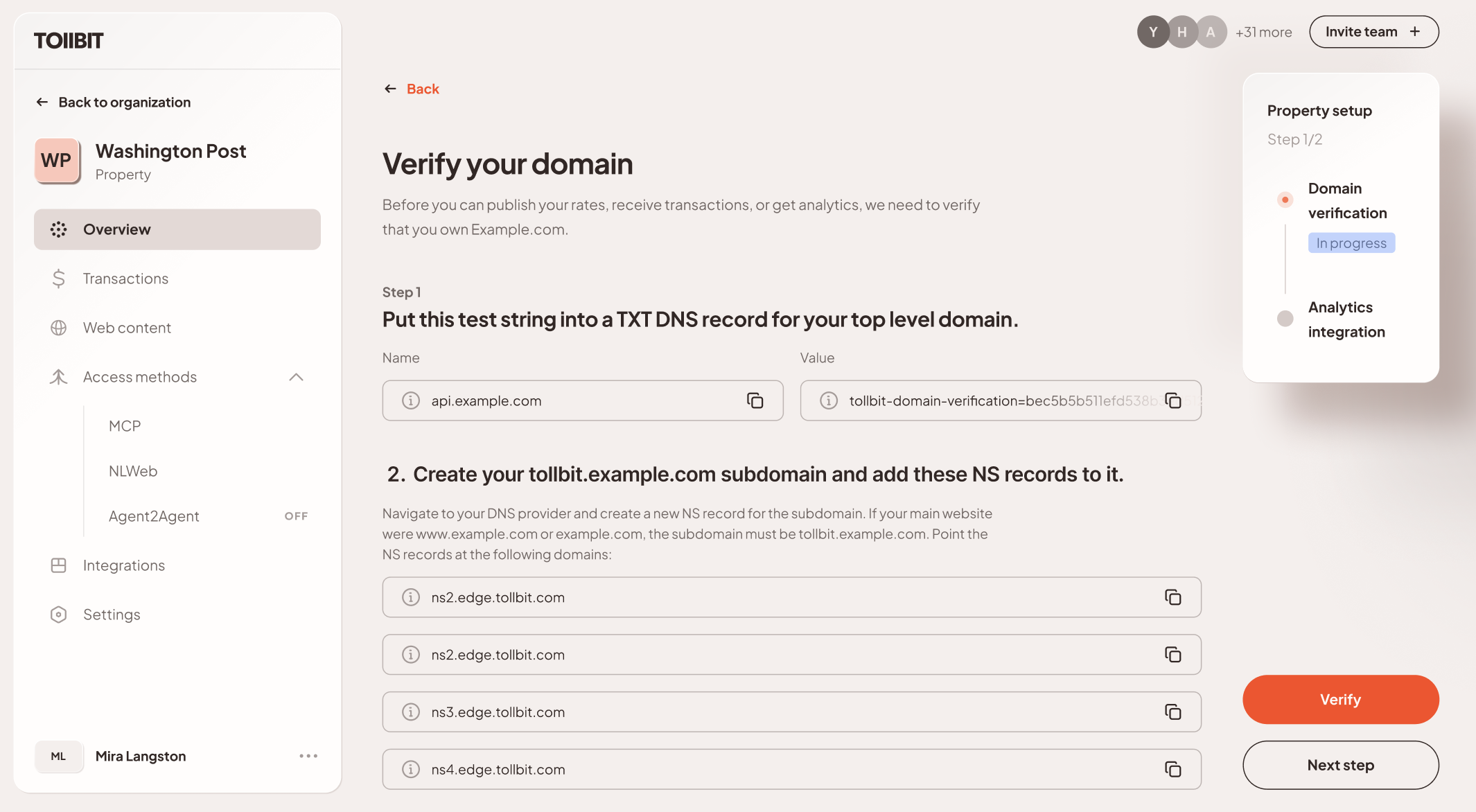
Step 2: The Agent Subdomain: We require the creation of a "tollbit" subdomain (e.g., tollbit.example.com). This subdomain will be the "agent" site, letting us serve up different content, manage authentication, enforce licenses and terms, etc.
1.3 Setting Up TollBit Analytics
One of the initial value props of the TollBit platform is analytics. Every site that onboards to TollBit is required to send us their HTTP logs. In return, we give them analytics tailored to helping website owners understand a new audience - an AI visitor.
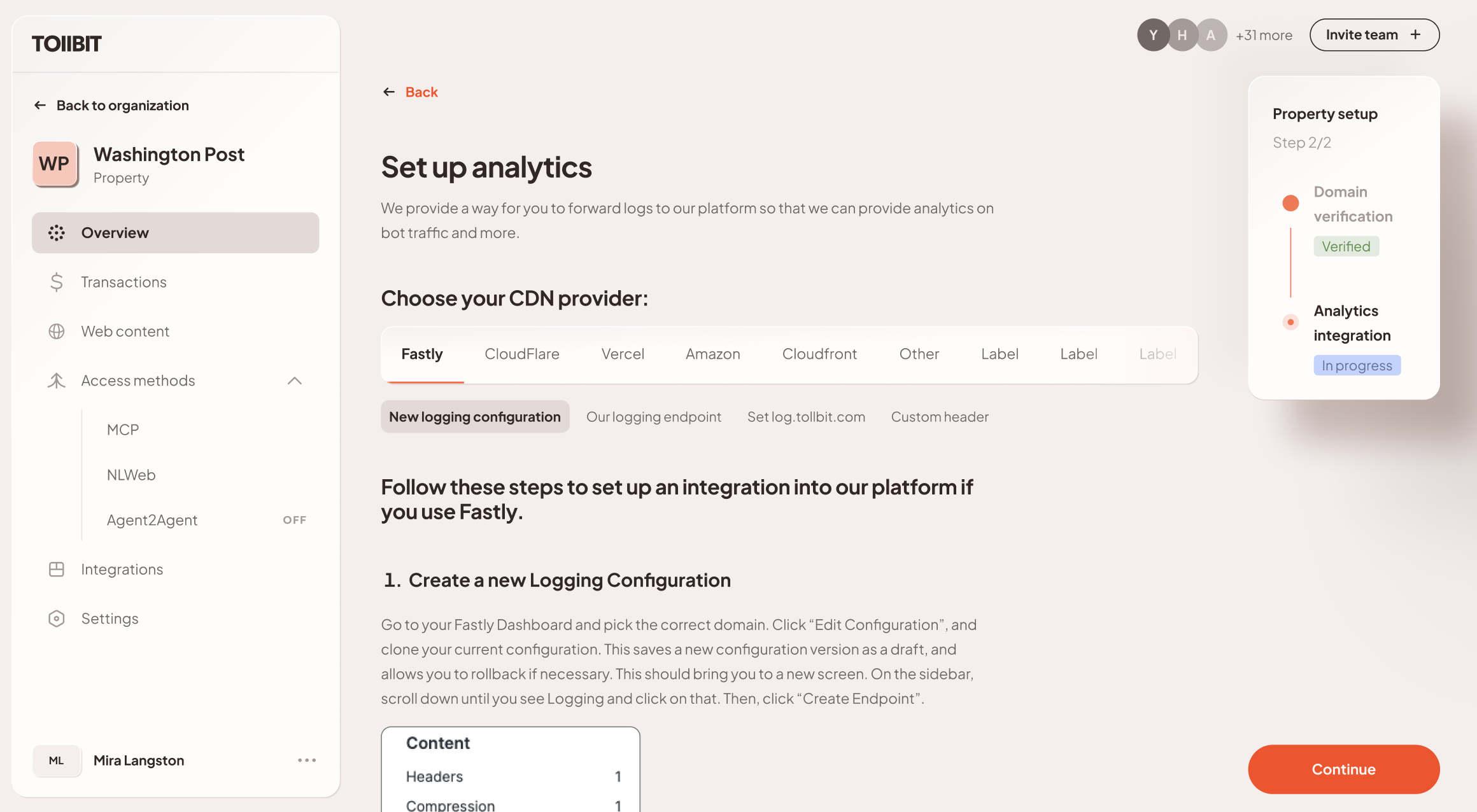
The TollBit platform has detailed documentation on how to set up log syncs for every major CDN vendor, allowing for smoother self-serve sign ups.
- Publisher configures a "Logpush" job to send HTTP access logs to TollBit's ingestion endpoint. This lets us see all traffic - both bot and human requests.
- Data Captured: Timestamp, URL Path, User Agent, Referrer, Status Code.
Starting Q4 2025, we also capture IP addresses after revising our Data Processing Agreement for all new publishers. Work is underway to update this for existing sites through Q1 2026.
1.4 Setting Up Payouts
TollBit uses Stripe Connected Accounts under the hood to handle payouts to publishers. Payouts will occur in the first couple days of the month, and will be for all transactions that took place in the previous month. More specifically, this will be from 00:00:00.000 UTC of the first day of the previous month, to 23:59:59.999 UTC of the last day of the previous month.
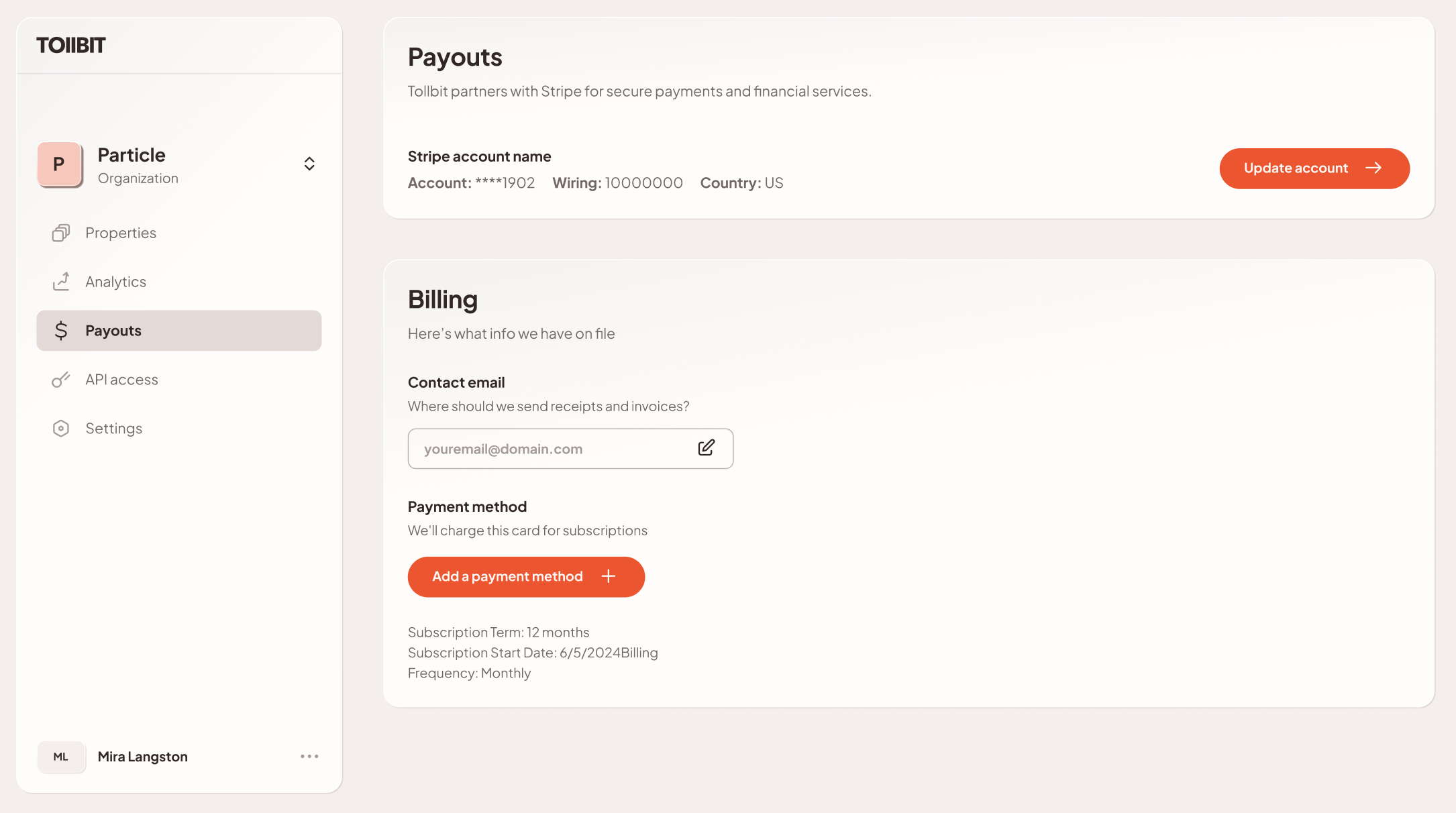
Publishers can only add one payout method per organization. This is fine for most orgs, but for those that prefer to keep accounting separate for subsets of their properties, they can create and manage multiple orgs, each with its own set of properties, and set payment information separate for each org.
Section 2: License Management Tools
Objective: To demonstrate how TollBit transforms static legal contracts into programmable logic. This section details how publishers define who can access their content, the permissions, and how existing off-platform deals are ledgered and implemented.
2.1 License Management Overview
TollBit turns licenses into programmatic implementations. Abstractly, every license encompasses: scope, price, and audience.
The License Dashboard: This is where publishers manage these relationships. It provides a unified view of all active agreements - whether it's a broad "Standard License" for the open market or a bespoke private license for a strategic AI partner. The dashboard transforms static legal contracts into API constraints that are enforced in real-time.
2.2 The Standard Licenses
For the vast majority of the 6000+ publishers on the platform, negotiating individual contracts with AI companies is impossible. To solve this liquidity problem, TollBit developed the TollBit Standard License.
There are two types of Standard Licenses on the platform:
-
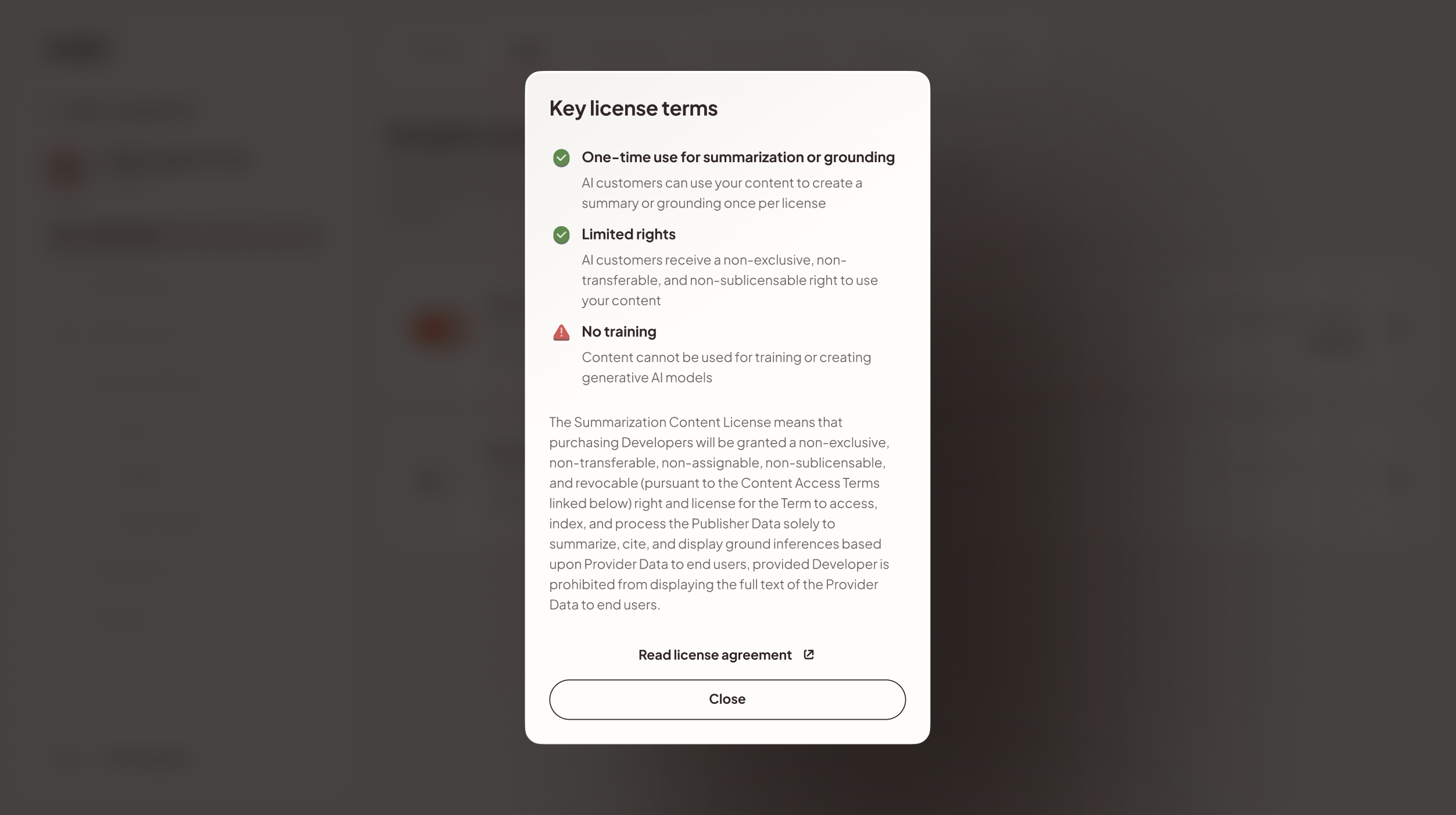
Summarization: The right to read, comprehend, and generate a summary/citation. This can be capped at character count or full length to load into context.
- Lower cost, higher volume
- Use case: grounding and inference in AI systems (RAG)
-
Full Display: The right to display the full text of the article to the end user.
- Higher cost, premium use case
- Use case: news aggregators or "Read Inside" experiences.
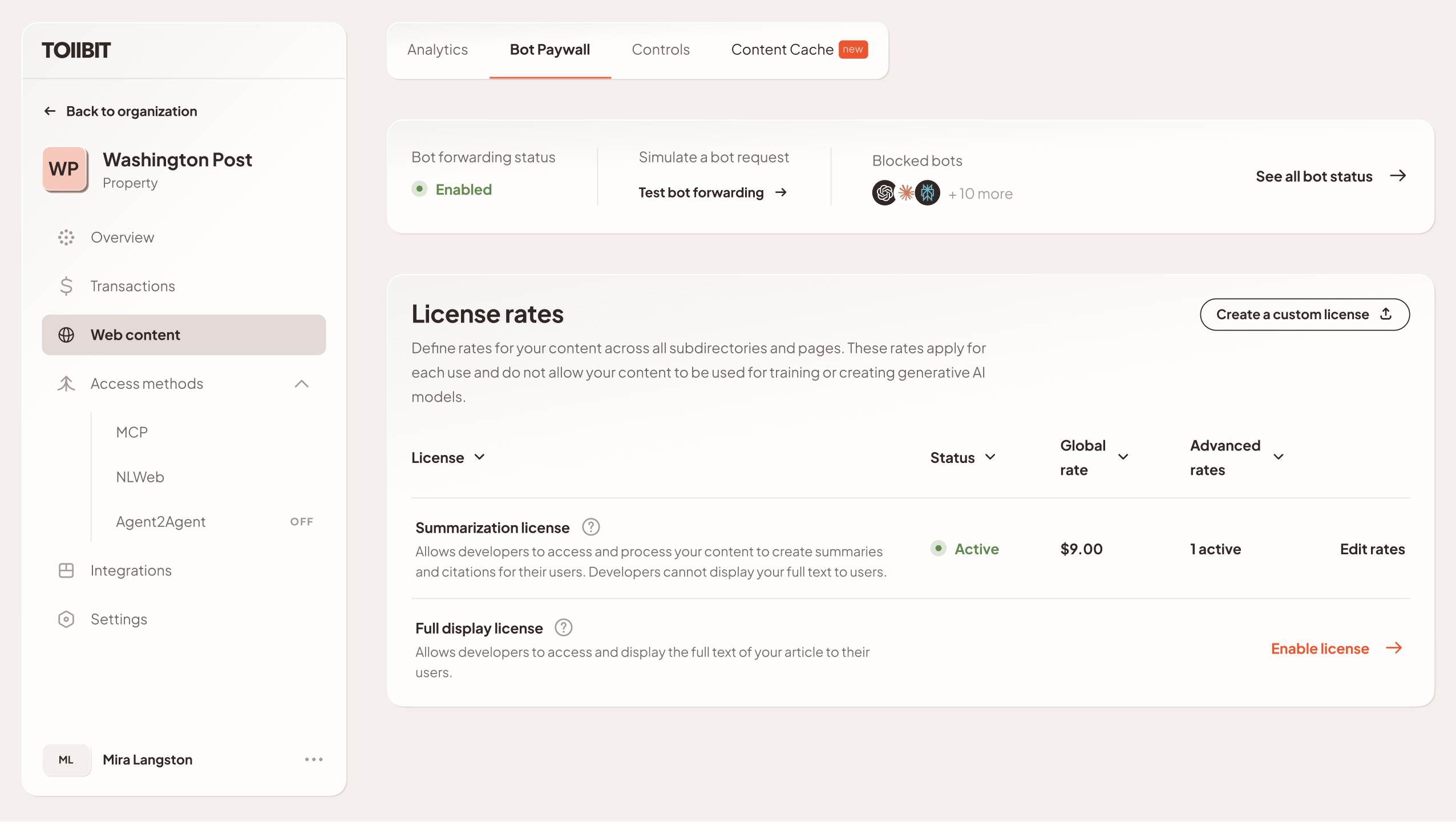
Admin members of the publisher org are required to click, view, then acknowledge acceptance of the license in order to activate it; TollBit tracks this, along with who makes changes to rates and rules on the platform.
These licenses are premapped to specific scopes that are programmatically exposed in the API as a license_scope object.
2.3 Custom License Agreements (Enterprise Partnerships)
Large enterprise publishers (e.g., Hearst, Gannett) often negotiate direct, bespoke agreements with major AI partners offline. The TollBit platform supports these arrangements and implements the governance/compliance requirements.
Step 1: License Definition - The publisher creates a new "Custom License" in the dashboard. They can upload the actual PDF of the agreement for record-keeping or use a placeholder reference (e.g., "Enterprise Partner License 2025").
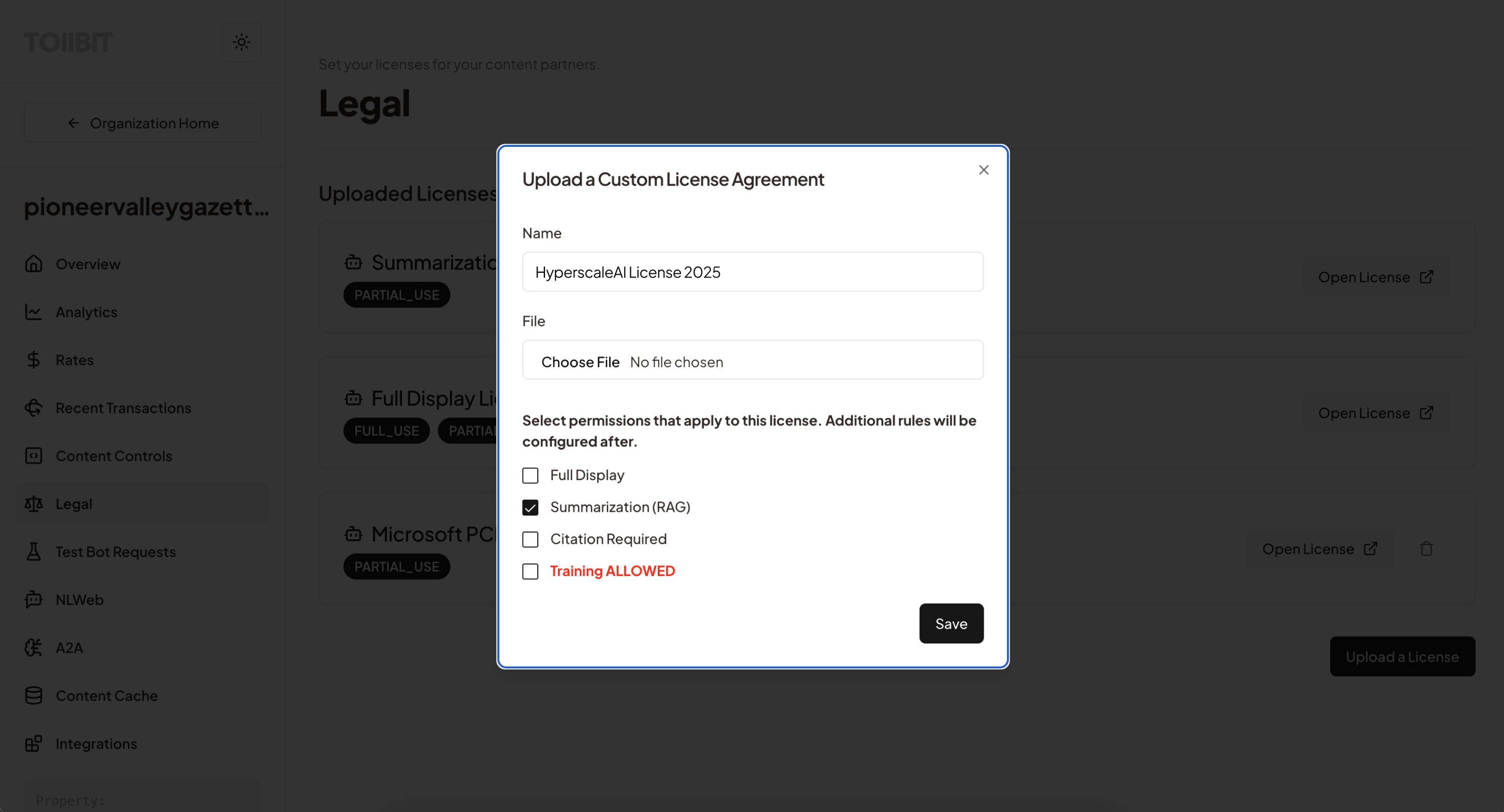
An org admin will be able to select which high level permission primitives apply to this license (full display, RAG, citation preference, training).
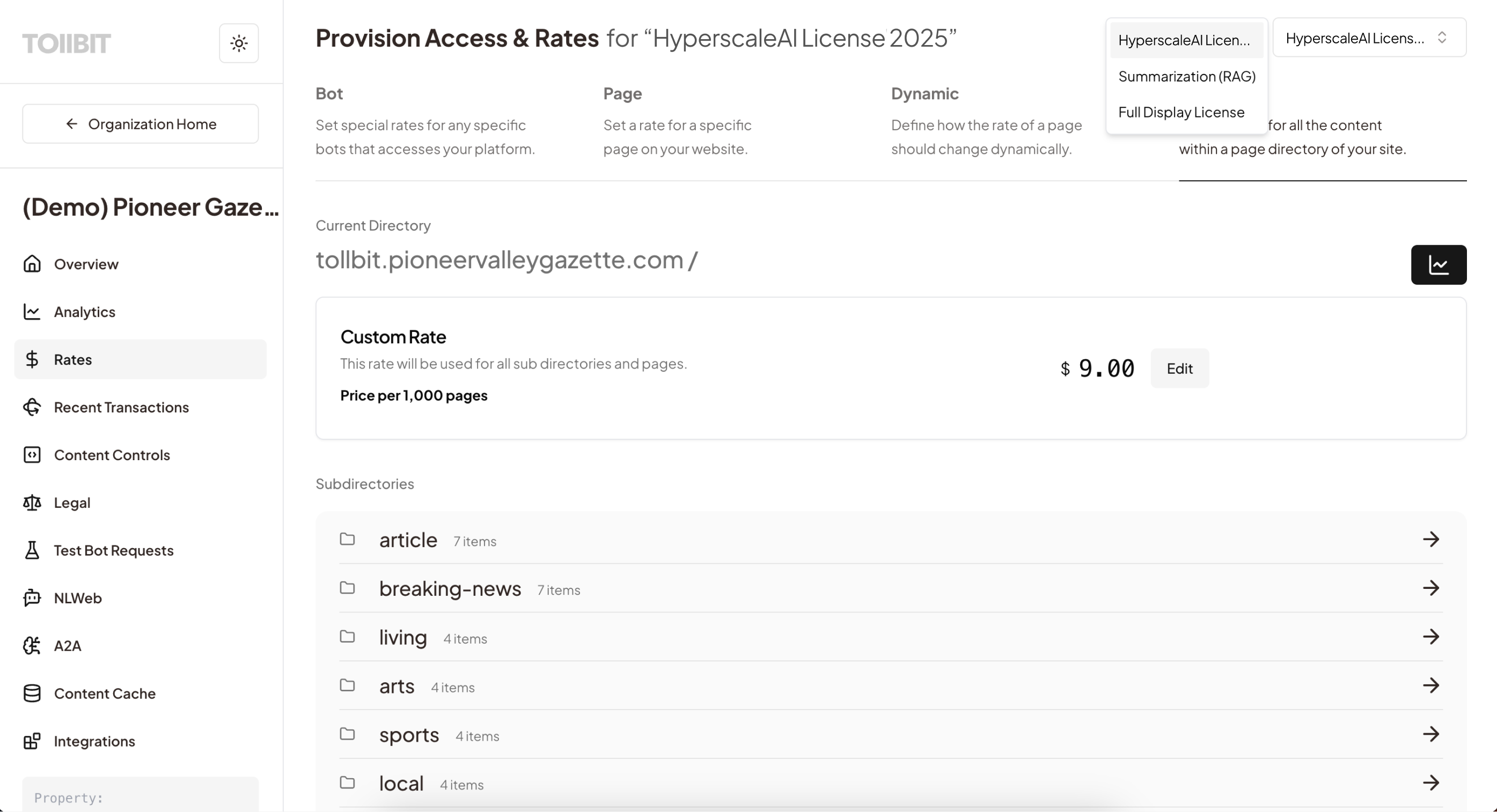
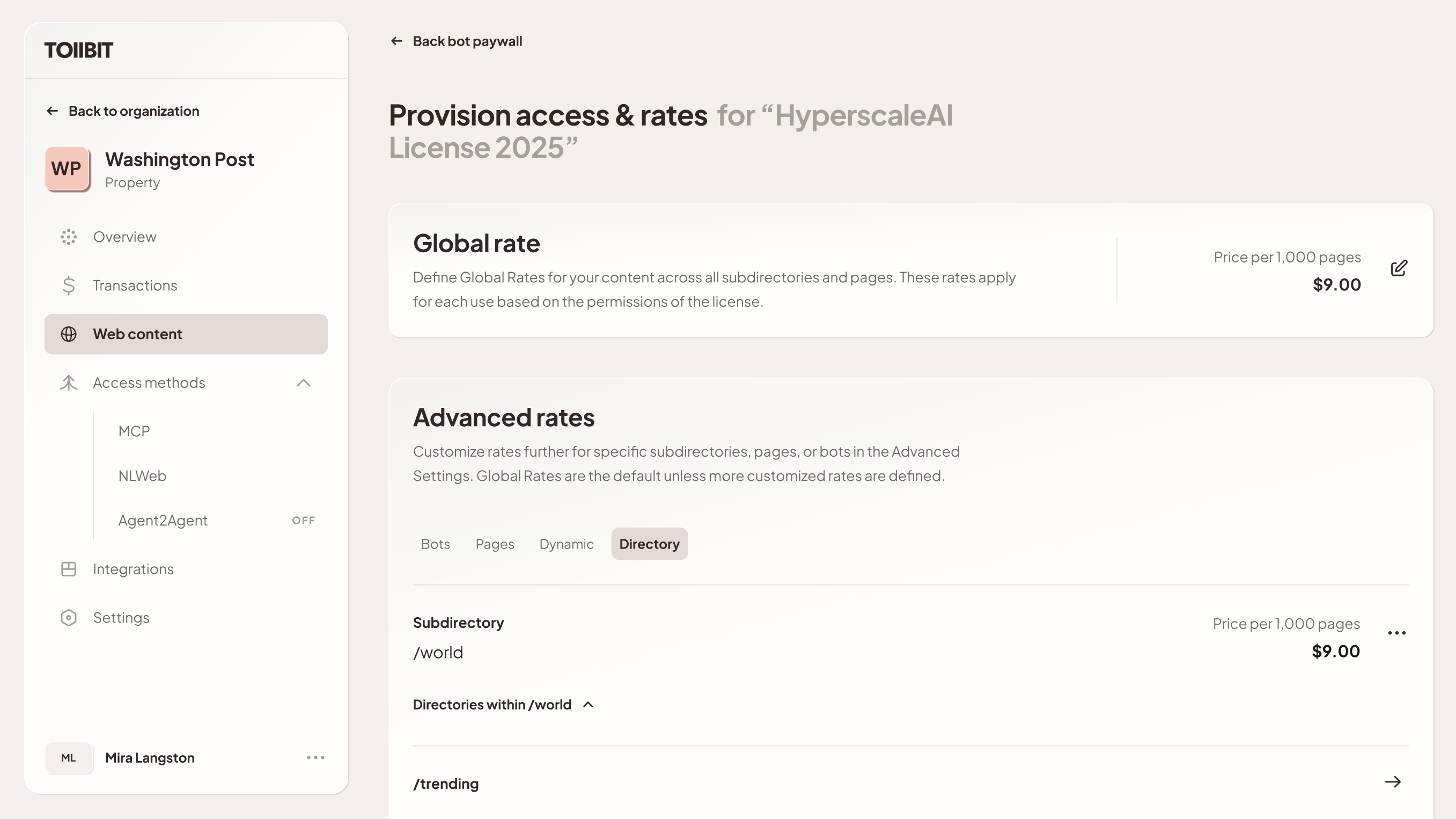
Step 2: Configuration of Rates & Rules: The publisher translates the contract terms into platform logic.
- Pricing: The publisher can set the specific usage rates and limits agreed upon in the deal, or set it to $0.00 if the deal involves a flat annual fee (allowing TollBit to act solely as the delivery, access and use ledger).
- Scope: The publisher defines which directories and pages apply to this specific license.
Current experience above, new experience (Q1 2026) below.
Step 3: Private Provisioning: Unlike the Standard License, this license is not public. The publisher explicitly provides access by whitelisting the AI partner's TollBit organization ID or verified user agents.
This ensures that only the AI partner can "see" this license in the API response and transact against this license ID. To the rest of the network, this license ID and its existence remains invisible.
2.4 Onboarding to AI companies' Publisher Programs
For AI companies with publisher programs, we can act as on-ramp for publishers to easily join their network. TollBit can provide discovery and enrollment for the middle and long tail of websites using the above workflows; this can also be limited to only publisher organizations that are invited.
Step 1: Opportunity Surface - In the TollBit platform, the publisher sees a dedicated card for the AI Partner Program. This surface displays the partner's marketing materials, value proposition, and specific T&Cs for review.
Step 2: Admin Acceptance - An org admin reviews the terms, and accompanying license. By clicking "Accept," they join the network of publishers for this program; TollBit tracks this e-signature.
Step 3: Automated Provisioning - Once the terms are accepted, the TollBit platform automatically generates the AI partner's specified license object under the hood for that property.
Section 3: Content & Rights Governance
Objective: To detail the technical mechanisms TollBit uses to "clean" the web page before it reaches the AI Partner's ingestion system. This layer ensures that the content delivered is not just legally licensed, but also free of irrelevant data (ads, tracking pixels), safety hazards (PII in comments), and unlicensed third-party assets (Getty Images, wire content).
3.1 The "Clean Context" Engine
Raw web HTML is noisy. It contains advertising scripts, tracking pixels, navigation footers, and user-generated comments that degrade the quality of RAG responses and waste context window tokens. TollBit acts as a sanitization layer.
Technical Implementation: This is done using TollBit DOM Filtering. Publishers can configure specific exclusion rules based on HTML structure. When content is accessed through the "tollbit." subdomain, our edge workers parse the DOM in real-time to strip these elements before the payload is constructed.
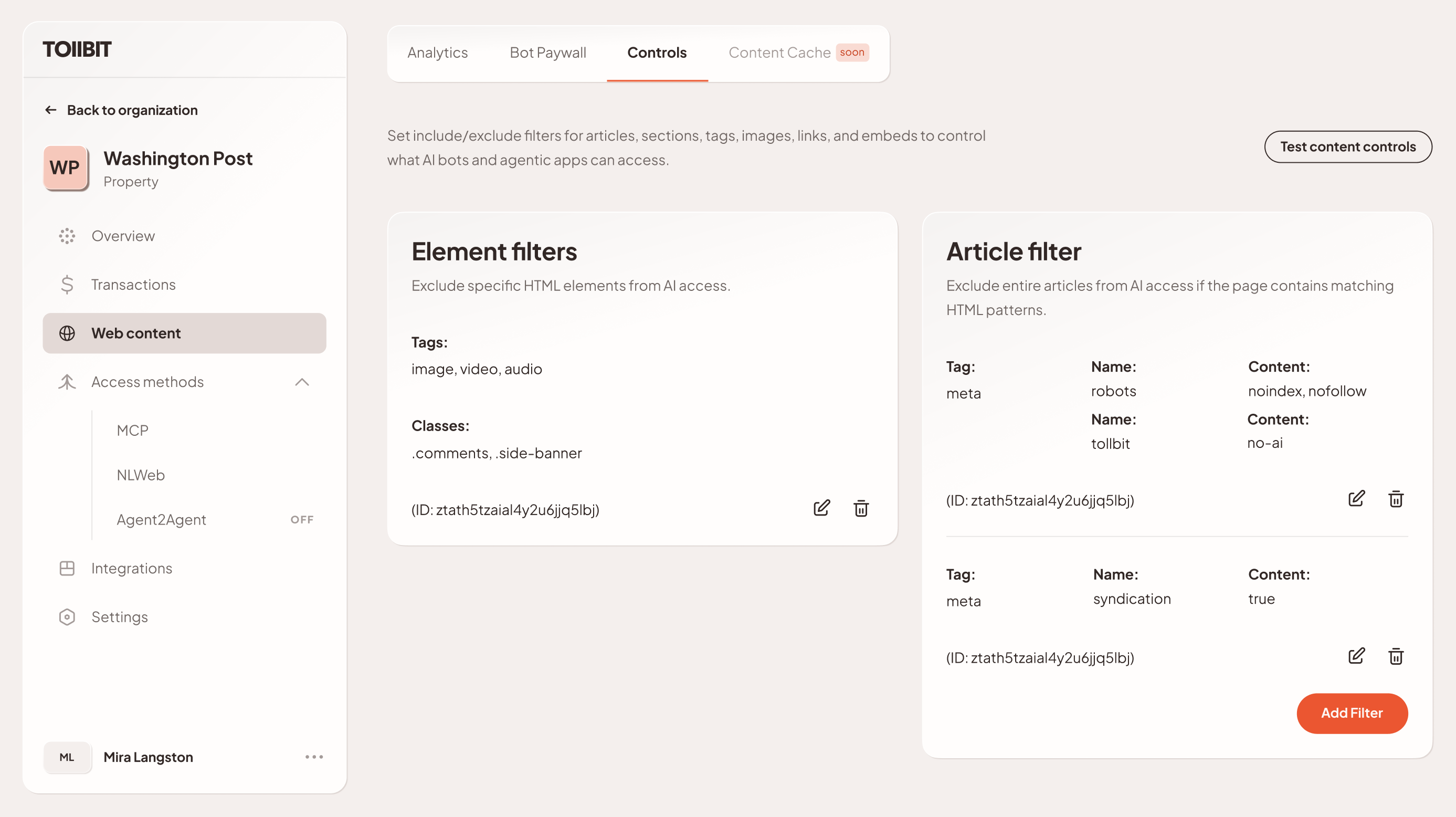
- Ad & tracker Removal: We automatically identify and strip standard ad tags and tracking pixels to ensure the agent receives only the semantic content.
- Arbitrary class exclusion: Publishers can define specific CSS selectors (e.g. '.comments-section', '.sponsored-content', '.sidebar-widget') to be removed. This ensures that certain components, "native advertising" or user comments are never ingested or used as RAG context.
3.2 Rights Management & Third-Party Asset Control
A major blocker for publishers and AI licensing is the "mixed rights" problem. A publisher may own the text of an article but not the accompanying image (from Getty/AP) or video.
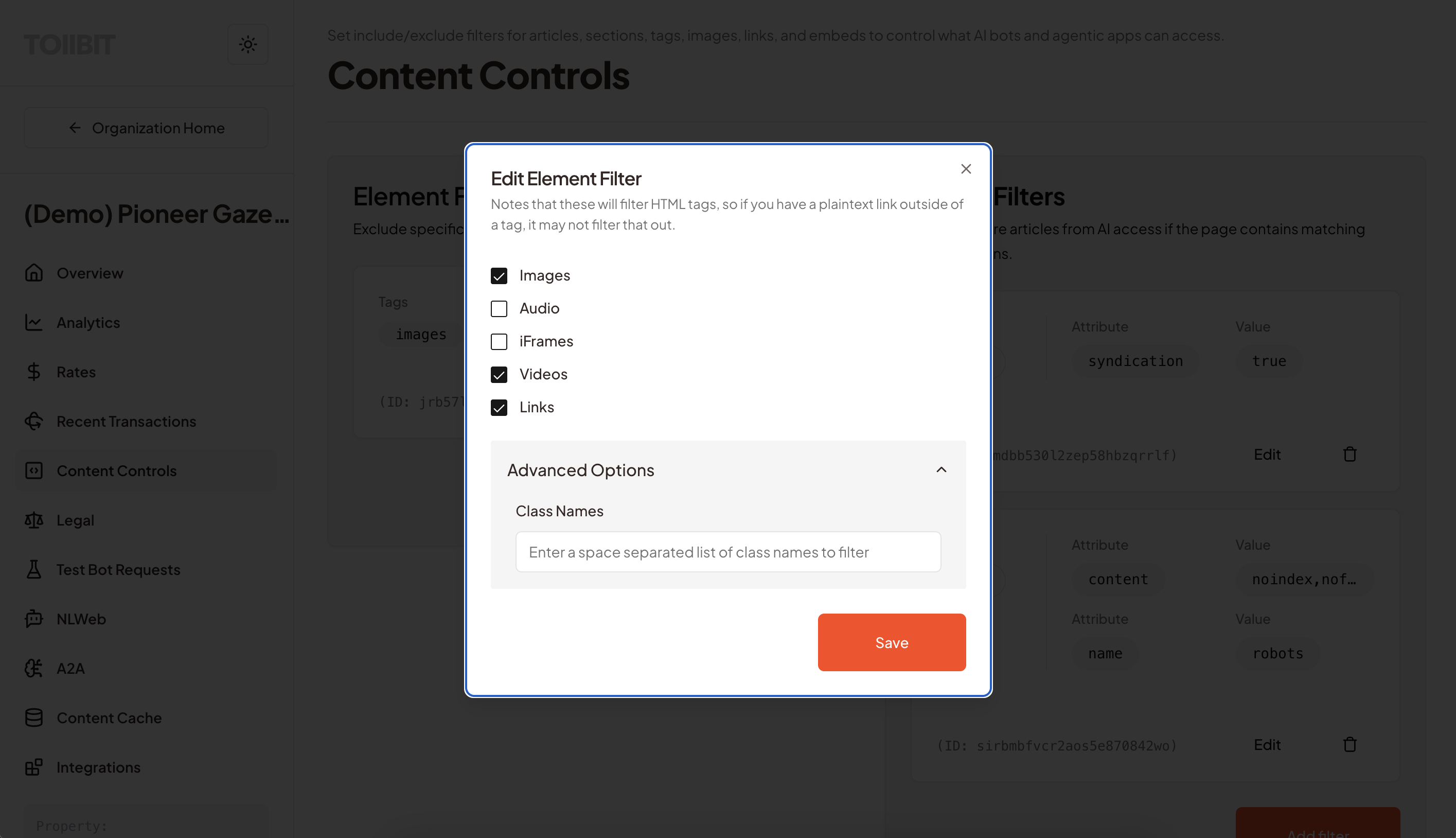
Technical Implementation: TollBit has the ability to program business logic to specific HTML/XML tags or MIME types at runtime.
- Whole-page exclusion: If a page contains a specific meta tag (e.g.
<meta name="syndication" content="true">), the API returns a '403 Restricted' response. This allows publishers to surgically remove wire and partner content easily. - Asset-level filtering (HTML/XML elements): Publishers can define filters that remove certain asset types which could be particularly problematic. For example, a publisher can strip any image or video tags that are in content. Coupled with the tag level filtering above, this can even allow publishers to strip out some images but leave their owned images on the page.
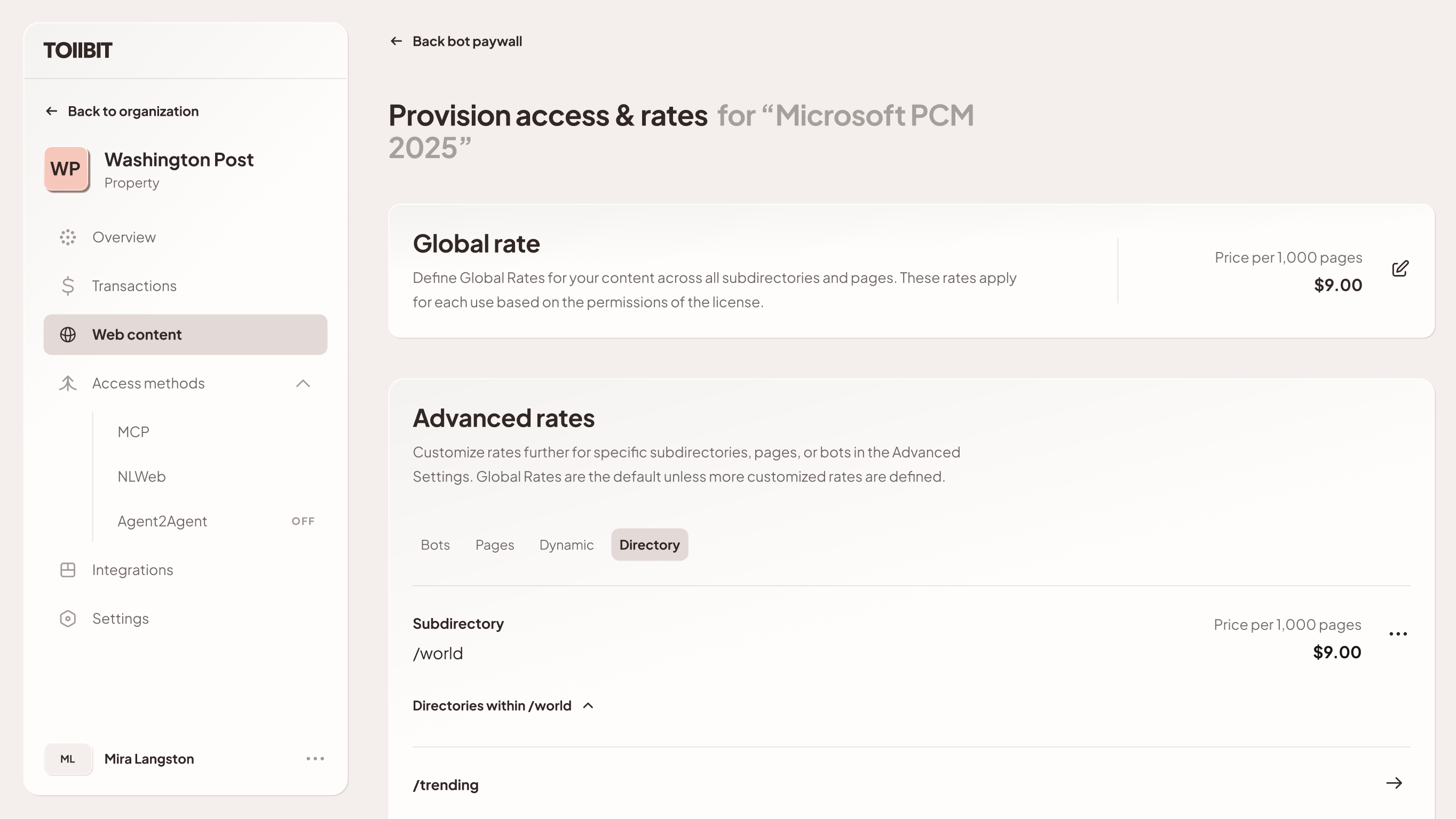
3.3 Directory & Path-Based Governance
Publishers rarely want to monetize their entire site uniformly. "Premium" content (e.g., Financial Advice) may have a different value or risk profile than news or sports.
To address this, publishers on TollBit define regex-based Inclusion/exclusion rulesets based on URL patterns.
- Excluded zones: Paths like '/login/', '/account/', or '/admin/' are hard-blocked at the TollBit proxy. Even if a crawler/agent attempts to fetch a URL in these directories, TollBit returns a '403 Forbidden', preventing accidental ingestion or use of sensitive pages.
- Combined with license management features, publishers can easily segment their site logic by directory for whatever their AI licensing strategy is.
Important nuance: Traditional governance relies on robots.txt, which is an eventually consistent system and has edge cases. A crawler might cache a 'robots' file for X hours. If a publisher blocks a directory during that window, the crawler (acting on stale data) might inadvertently ingest restricted content, creating legal liability.
Unlike robots.txt, which relies on the crawler to re-fetch and parse a file, the rules on TollBit are applied at the proxy layer instantly. If a publisher adds a new "Investigative Report" section to the exclusion list, access is cut off for all subsequent API calls, ensuring immediate compliance. TollBit also maintains an immutable audit trail; we log exactly when a rule was created and when every access attempt occurred.
3.4 Embargos & Blackouts
News is time-sensitive. Some publishers on TollBit have embargo windows (exclusive breaking news, election results) where they want to maximize direct human traffic before allowing AI usage. TollBit allows for programmatic control over when content becomes available to the AI ecosystem.
TollBit solves this by using metadata from the page that the publisher configures, such as <meta name="tollbit_publish_time" content="1764901394"> (or any HTML selector that the publisher specifies to be parsed by us) on sensitive pages. Publishers can set "time decay" rules relative to this Unix timestamp in the platform.
Instead of a hard 403 error (which might confuse a crawler into thinking the page is broken), TollBit exposes explicit availability metadata in the API response. We also support webhook notifications to notify AI partners when content becomes available for use.
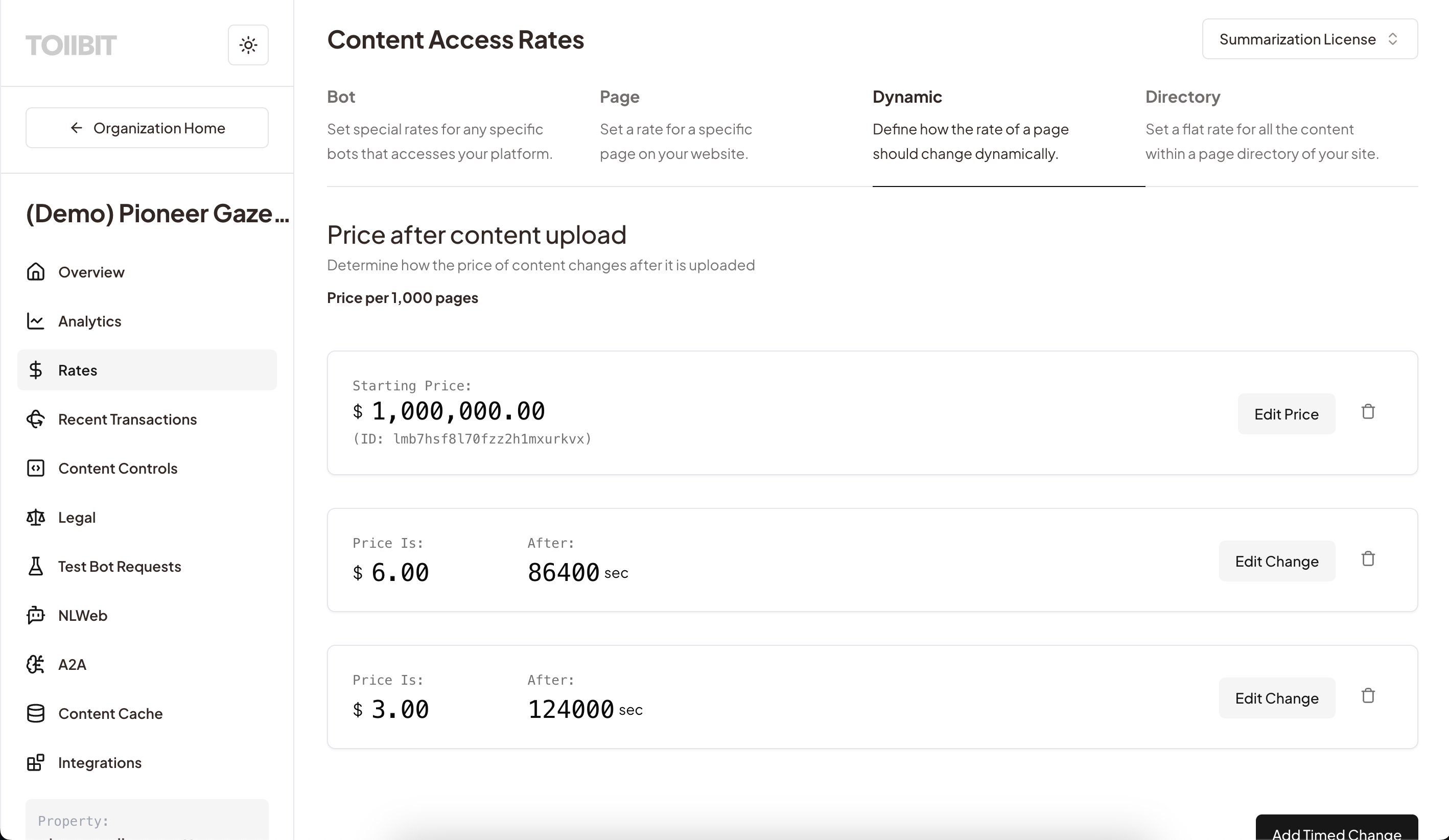
The same feature can also be used by publishers to charge a premium for newer content for RAG use and citation, with a time decay as the news becomes stale.
3.5 Content Transformation
Ingesting the raw web requires significant pre-processing to separate signal from noise. The TollBit API performs extraction and normalization, delivering a clean, structured payload optimized for AI context windows.
TollBit transforms the raw HTML into machine-readable formats based on the 'format' specified in the request to the tollbit subdomain; this format could be HTML or markdown.
- Markdown conversion: We strip non-semantic HTML tags (scripts, styles, iframes, divs) and convert the body content into clean markdown. This preserves the document hierarchy (headers, lists, tables, bolding) while removing the markup overhead.
- JSON-LD & Schema Extraction (coming Q1): If the page contains structured data (e.g. Schema.org/NewsArticle, Recipe, or Product), we extract and serialize these objects into a dedicated field in the API response.
3.6 Enriching Content
If the publisher allows it, TollBit can go beyond just transforming content on page. We have the ability to fetch from underlying APIs and expose interactive agent components embedded within the page as part of the response.
API integration: For partners with rich metadata that isn't rendered on the public page, TollBit integrates directly with their backend APIs. Publishers provide us API credentials and we build logic to fetch additional metadata. This is how we integrate with The Associated Press.
On content fetch, TollBit simultaneously queries the publisher's API to fetch structured metadata (e.g. "Geolocation Tags," "Ticker Symbols") and merge it into the response. This gives agents data that a human browser does not see.
Agent Apps (Interactive Widgets): To improve interactions, visualizations and improve engagement, TollBit created the open source Agent Apps Project (https://agentapps.dev). This is an easy way for sites to expose interactive components that are specific to pages, so that they are contextually relevant. Any Agent Apps that are specified on the page are added to the response TollBit sends back. An AI app can render these in responses to improve engagement by rendering UI components.
Publishers can create these components using regular web development, hosted on their existing site (e.g. a mortgage calculator, election map, or podcast player). This bypasses the added complexity from frameworks like MCP, boosting ease of creation and supply. Since these are just URLs, monetization is also supported using TollBit Tokens.
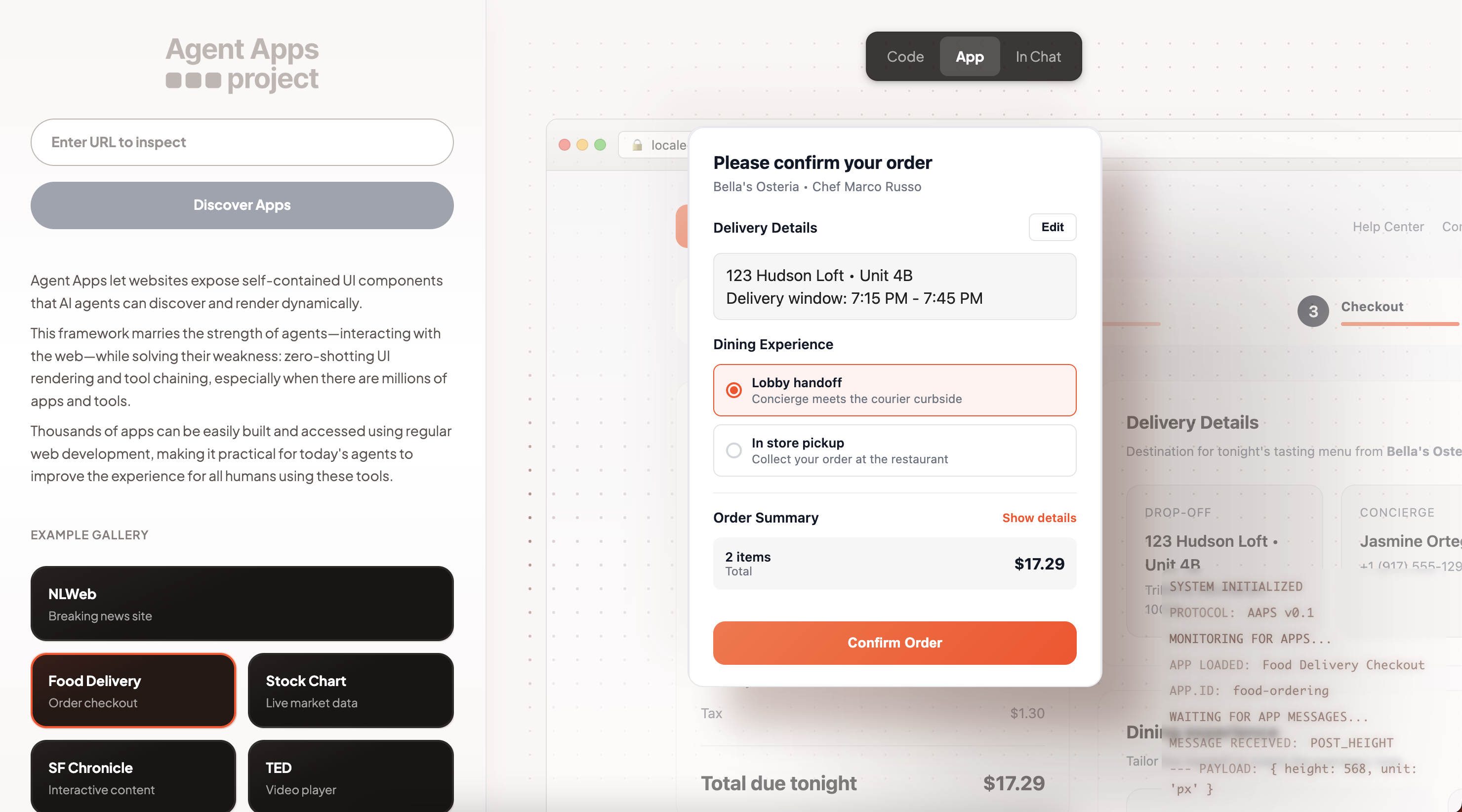
Section 4: Pricing & Value Signals
Objective: The economics of the AI-Publisher ecosystem are still in their infancy; there is no established "fair market value" for a RAG use or citation. TollBit provides the granular infrastructure required to move the industry from opaque, flat contracts to a data driven market price. The platform enables both sides (publishers and AI apps) to signal value, test elasticity, and eventually discover the true clearing price for a piece of content.
4.1 Vectors of Value
Not all content is created equal - a breaking financial report has a different utility than an old lifestyle blog post. TollBit provides publishers with a set of programmable vectors to signal this differential value to the ecosystem.
TollBit provides publishers with programmable vectors to signal differential value to the ecosystem, by assigning pricing overrides:
-
Path-Based Signals (specific pages): Publishers can assign unique value signals to specific high-value pages.
- Example: A publisher can set a premium rate for a specific page that contains a live updating sports score URL.
-
Directory-Based Signals (category based): Publishers can segment their pricing logic by content vertical using directory patterns.
- Example: A publisher can assign a higher value to '/business/' and '/tech/' directories (high commercial utility) while setting a lower standard rate for '/sports/' or '/lifestyle/'.
-
Temporal signals (time based): Value often correlates with freshness. TollBit's engine can ingest publication timestamps and apply dynamic logic.
- Example: A publisher can configure a decay curve where content carries a premium signal for the first 24 hours (during the news cycle peak) and automatically reverts to a base rate afterwards.
4.2 Hyperscaler Economics
For hyperscale AI companies, "retail" pricing models break down. A platform serving billions of citations requires mechanisms for wholesale economics. TollBit's pricing engine is designed to support these high-volume relationships.
We have two mechanisms on the platform to support this:
-
Volume discounts: It is possible to set a volume discount on the platform to any rate set by a publisher. This discount is set on a developer or user agent basis. This ensures that HyperscaleAI and its agents will see the discounted pricing instead of the public rate card when asking for rates. Today this is a flat discount applied on the rate set by the publisher, but it is a sufficient starting point when combined with the differential value to find true FMV. Tiered volume discounts is in the backlog.
-
Private rate cards: For strategic AI partners that publishers have a deal with, the public market price is irrelevant. We configure $0 pricing overrides to ensure the AI partner's account (or even a specified subset of their user agents) are not billed but still ensures compliance and ledgering for these deals.
This allows some HyperscaleAI to negotiate strategic deals while still utilizing the TollBit infrastructure for delivery, compliance, and analytics. This way, the API, ruleset, integration remains consistent across private deals or marketplace publisher content.
4.3 On-behalf-of Access
An AI company may not be building an app but a platform that needs to serve thousands of enterprise developers and AI builders. It is possible that some of these downstream developers (perhaps a hedge fund) may have their own direct relationships with publishers that differ from market terms. TollBit supports this complex, multi-layered identity model.
The developer can give you their TollBit credentials (org ID + user agent + API key). When your platform makes a request to the TollBit API, you can supply the developer's credentials in the request. The publisher, who is already on TollBit, will have configured the terms of their one-off deal.
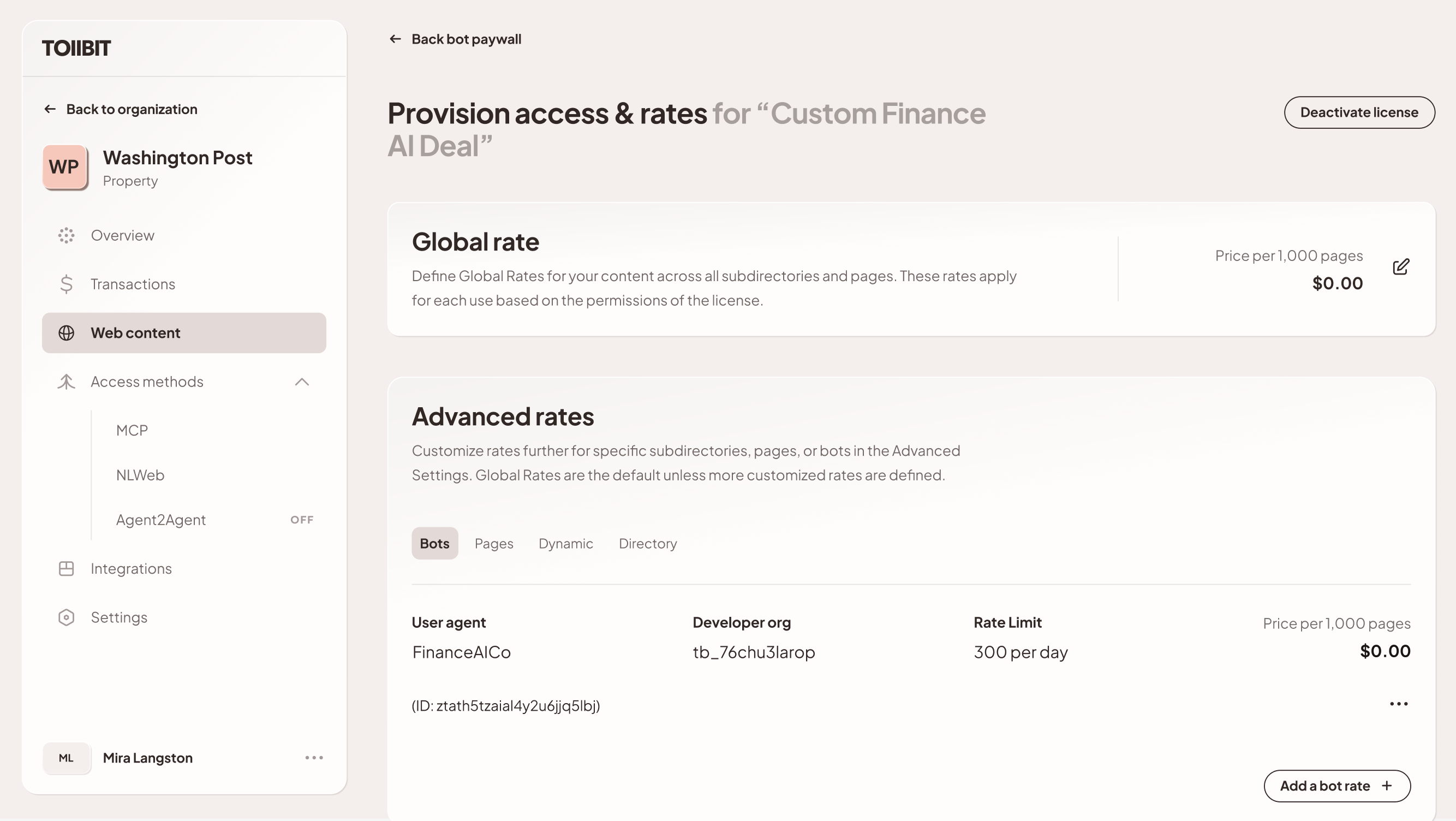
The license_scope response we return to your platform would contain this bespoke term to the developer.
This ensures the TollBit API returns the content and rights based on that specific developer's deal with the publisher, while still using your platform infrastructure for the fetch.
4.4 The Future: Bidding & Dynamic Demand
The current model of fixed rate cards is a starting point, not the end state. As the ecosystem matures, pricing will likely evolve into a liquid market similar to ad tech. TollBit's architecture is built to support this evolution.
"Fixed price" to "floor price": The rate cards publishers set today may evolve into floor prices in future auction models. Instead of asking for the price, the API may allow agents to bid on the price. This is not practical today because no one knows what the FMV is. The right analogy is perhaps that we are transitioning from the direct sales ad world to the very early days of programmatic; RTB is way down the line.
Because TollBit ingests server-side logs from all onboarded publishers, we have a cross-network view of global content demand. This data allows us to detect demand spikes (e.g., a breaking news story) and dynamically adjust value signals in real-time.
For AI Companies
Section 5: Integration Models
AI Partners on TollBit have vastly different architectures for ingestion and inference. Some require real-time fetching for RAG; others have created pre-indexed knowledge graphs and critical inference SLAs. Or perhaps you are a platform that wants the ability for your developers to license content for RAG. TollBit provides flexible integration solutions that support these varied requirements while ensuring compliance and remuneration. However, the patterns generally fall into three broad integration models.
5.1 The Proxy Integration (Real-Time Fetching)
Best for AI partners who want "Clean Context" (markdown) delivered instantly without maintaining their own rendering/cleaning infrastructure.
This is the primary integration path for real-time RAG. Agents fetch content directly via the TollBit subdomain infrastructure (i.e. the "agent site"). This acts as a gateway that handles authentication, licensing, filtration, and formatting at the edge.
The Workflow:
-
Token Minting: The Partner's ingestion service mints a Licensing Token (a signed JWT). This token acts as a micro-contract, declaring the licenseCuid and a maxPriceMicros bid to prevent overspending.
-
The Request: The Agent makes a GET request to the publisher's TollBit subdomain, appending the token.
GET https://tollbit.publisher.com/article/deep-dive-analysis
Header: TollBitToken: <SIGNED_JWT>
Header: TollBitOrgCuid: <ORG_CUID>
Header: User-Agent: Enterprise-Partner-Agent
-
Edge Validation: The TollBit Gateway validates the signature, checks the license validity, and ensures the price meets the current rate.
-
Response (RAG-Ready): Upon success, TollBit returns the transformed content (cleaned markdown, stripped of ads/PII, all rights cleared).
Transactions are not logged, nor is anyone billed, until the token is actually accepted and a 200 OK response is delivered.
5.2 The Metering Integration (Async Reporting)
For AI companies with high-speed internal crawlers who prioritize inference speed and want to decouple remuneration from the generation latency loop.
For AI companies that prefer to use their own crawling infrastructure, TollBit offers Metering APIs. This allows them to use their existing index and internal cache for inference and asynchronously "report" usage for billing. Payments and ledgering are only recorded to publishers on TollBit, according to the rules provisioned. Payments for content the publisher does not have rights to are rejected.
Technical Implementation: An AI partner can submit batch usage events to the TollBit Metering API. These events are aggregated by TollBit to ledger content usage. This endpoint supports both real-time one-off reports and batched reporting for efficiency.
POST https://gateway.tollbit.com/tollbit/dev/v2/transactions/selfReport
Header: TollbitKey: <TOLLBIT_API_KEY>
Header: User-Agent: <demand_org_user_agent>
The API returns the explicit financial calculation for the reported usage, confirming the transaction was ledgered.
The metadata field is a powerful tool for feedback to publishers to inform content strategy. AI companies can pass in any arbitrary maps (e.g., query_topic, other_citations, product_surface) of their own choosing back to publishers. This metadata is parsed by us and surfaced in TollBit Analytics.
This data helps publishers understand why their content was chosen (e.g., "My content is highly cited for 'Local Politics' queries"), encouraging them to produce more high-value content for the ecosystem.
5.3 Hybrid Discovery
For AI companies with a world-class search index (for finding URLs) but who need a compliant way to "read" and transact for RAG.
Many partners are excellent at identifying which URLs are relevant (Discovery) but face legal ambiguity when using cached HTML for RAG. This model allows the Partner to use their own Search Index for finding content, and TollBit for reading it.
The Workflow:
-
Discovery (Internal Index): The Partner's search engine identifies relevant URLs (e.g., vox.com/article/123) based on a user query.
-
The Content Filter: The AI Partner checks these URLs against the TollBit Bulk License Scope endpoint. This endpoint accepts an array of URLs and returns their license status and rates.
-
Fetch & Hydration: For the URLs in the TollBit network, the Agent executes a Content Fetch from the by prepending "tollbit." to the URL.
- Input: The URL found by the search engine.
- Output: A clean, licensed markdown payload with rights explicitly cleared.
-
Cache Update: The Partner can store this compliant version in a dedicated "RAG cache" to update their previously indexed content.
The exact integration model will depend on each AI company's infrastructure, risk and compliance requirements, but generally is composed of TollBit products for the above models.
Section 6: Content Ingestion & Access
Objective: For AI companies building large-scale knowledge graphs or datasets, we have solutions for efficiently ingesting and maintaining millions of licensed documents. TollBit provides a suite of ingestion tools designed to reduce crawler overhead, eliminate redundant recursion, and ensure index freshness without constant polling.
6.1 The TollBit Content Cache (Rights-Cleared Crawling)
For AI companies who want to crawl a "clean" publisher network where every hit is guaranteed to be licensed and formatted.
It is necessary to crawl the web in order to know where great content lives. This allows AI companies to speed up inference by building a persistent index or knowledge graph rather than fetching content just-in-time. The TollBit Content Cache allows these partners to crawl the tollbit agent sites instead of the publisher's main site. The Content Cache can also be hit multiple times a second without driving up CDN and compute costs for publishers.
By pointing crawlers at the TollBit infrastructure (e.g., https://tollbit.npr.com) rather than the open web, AI Partners achieve two distinct advantages:
-
Liability insulation: The crawler cannot ingest unlicensed content. If a publisher has not opted into the Partner Program, or if a specific directory is excluded, the TollBit edge returns a 403 Forbidden before the data ever touches the Partner's servers.
-
Optimized ingestion: Instead of downloading heavy, raw HTML (filled with DOM bloat, ads, and scripts) and processing it locally, the Partner crawls pre-processed, lightweight markdown. This significantly reduces ingress bandwidth and storage costs.
TollBit handles the complexity of caching and validation, ensuring AI companies always receive the most up-to-date licensed version of the content.
6.2 The Content Catalog (Flattened Topology)
Best for eliminating the need for recursive crawling and complex sitemap parsing.
Traditional crawling is expensive because it requires "walking the tree," recursively fetching sitemaps and index pages to find the actual articles (leaf nodes). The Content Catalog simplifies this by flattening the publisher site topology.
Instead of parsing complex XML sitemap trees, the Partner accesses a paginated endpoint on the publisher's TollBit subdomain. This gives a flat, paginated list of all valid "leaf" URLs (articles) available for licensing, ready to be ingested through our API.
This eliminates thousands of unnecessary requests to non-content pages (category pages, directories, archives) and allows the Partner's ingestion system to focus 100% of its compute on indexing high-value content nodes.
6.3 Webhook Notifications
Best used in conjunction with above solutions for maintaining real-time index freshness without polling.
For news and time-sensitive content, polling is inefficient for both AI apps and publishers. TollBit offers a push-based notification system to keep AI companies in sync with the publisher's CMS, including for updates on pricing, content on page and rights updates.
The Workflow: The AI Partner registers a webhook endpoint with TollBit. When a publisher in the Partner Program creates or updates content:
- TollBit is notified or detects a new article or update to an article. Or a publisher makes an update to the licensing ruleset.
- TollBit fires a webhook event to their ingestion service containing the URL and the type of change.
- The AI system can immediately queue a fetch for that specific URL, ensuring their RAG responses reflect breaking news mere seconds after publication.
6.4 The Fetch Endpoint (Accessing the Agent Site)
The technical interface for accessing RAG-ready content from publishers.
Regardless of whether you are using the Proxy Model or Hybrid Discovery, the actual mechanism for retrieving content is the fetch action. Every publisher on the platform has a dedicated "Agent Site" (e.g., https://tollbit.pbs.org) that serves machine-optimized content instead of human-facing HTML.
Access is performed via a standard GET request to the publisher's tollbit subdomain, mirroring the path of the original article.
GET https://tollbit.{publisher_domain}/{original_path}
Header: TollBitToken: <SIGNED_JWT>
Header: TollBitOrgCuid: <ORG_CUID>
Header: User-Agent: Enterprise-Partner-Agent
The Response (the "Clean Context" Payload): Unlike the raw origin site, the Fetch Endpoint does not return messy HTML. It invokes TollBit's Clean Context Engine to return a payload optimized for context windows:
- Non-semantic HTML (scripts, styles, ads, nav bars) is stripped. The body content is converted to clean markdown or HTML.
- Third-party assets (e.g., licensed wire content or Getty images) are automatically redacted based on the publisher's governance rules before the payload is generated.
- If the page contains Schema.org objects (e.g., NewsArticle, Recipe), these are extracted and serialized in a dedicated metadata field.
- Optional integration to publisher APIs or embeddable Agent Apps to add metadata with the page response.
Error states:
- 402 Payment Required: The maxPriceMicros in the token was lower than the current price.
- 403 Forbidden: The licenseCuid in the token is not valid (e.g. the publisher revoked that specific license version, or does not support that license term).
The TollBit Agent Site ensures that your AI app or agent receives a rights-cleared payload through a standardized integration regardless of the underlying CMS or frontend architecture of the publisher.
Section 7: Security & Authentication
Objective: This section details the technical specifications for accessing and consuming content from the TollBit network of Agent Sites. The architecture uses a signed token model to ensure secure access to public-facing publisher subdomains without exposing sensitive API keys.
7.1 The TollBit Token (Signed JWTs)
TollBit sets up a parallel gateway at publisher domains (the Agent Site). This means crawlers and agents fetch content directly from publisher subdomains (e.g. https://tollbit.rollingstone.com/...). Standard API keys cannot be used, as they would be exposed in transit or logs and are vulnerable to replay attacks. Instead, we use short-lived, cryptographically signed TollBit Tokens.
The Token Mechanism: Before accessing the Agent Site content, an ingestion service or AI agent generates a signed JWT (JSON Web Token) using its TollBit API key. This token declares the intent and identity of the request.
The token contains all necessary authorization logic, allowing our edge to validate requests in milliseconds without database lookups.
All requests are validated against the public key of the AI partner's Organization ID. The gateway checks the userAgent claim against the registered agent profiles in the Partner's account. This ensures that the agent claiming to be this user-agent actually belongs to your organization and is not a spoofer.
Note: The user-agent in the Token is what is validated for billing and permissions, not the HTTP Header, preventing header spoofing.
7.2 Token Types & Claims
The TollBit Token varies depending on the intent of the request. The claims included in the signed JWT determine the scope (indexing, licensing or access), acknowledgement of license (if applicable), and agent identity.
Crawling tokens: This token is used when the intent is to simply crawl the TollBit network of sites for ingestion, indexing, or checking freshness. The same token can be used for the entire crawl session without regenerating.
The claims included are:
- tld: The domain you are crawling.
- userAgent: Your user agent representing this request. This user agent MUST belong to your org.
- exp: The expiration time of this token. You set this value, we simply check that it has not expired.
This crawl token allows the TollBit Gateway to cryptographically validate your crawler identity. No transaction is recorded, no fee is charged when you enter the network with a crawling token type.
Licensing/transaction token: This token is used when the intent is to fetch the full content payload for RAG or display. This token acts as a micro-contract and is generated per request.
The claims included are:
- url: The specific page url for this token is for. Prevents replay attacks.
- userAgent: Your user agent representing this request. This user agent MUST belong to your org.
- maxPriceMicros: The price (in micros) that was quoted, to guard against race conditions.
- licenseCuid: Referenced in the license scope response. Knowing this value requires the developer to have acknowledged this license and its terms.
- permission: Referenced in the license scope response. TollBit checks that the license cuid/permission combo is valid.
Access with this token type triggers a ledger event and financial transaction upon a successful 200 OK response.
Access token: This token is used when the intent is to access a TollBit Agent Optimized Site for browser automation tasks; no licensing is involved. This token is generated per request.
The claims included are:
- url: The specific page url for this token is for. Prevents replay attacks.
- userAgent: Your user agent representing this request. This user agent MUST belong to your org.
- maxPriceMicros: The price (in micros) that was quoted, to guard against race conditions. This is set to 0 for sites that don't charge for agentic access.
Access with this token type triggers a ledger event and financial transaction upon a successful 200 OK response.
Section 8: Analytics & Ledgering
Objective: TollBit provides an immutable ledger of every transaction in the ecosystem. Beyond billing, TollBit Analytics closes the loop and enables new business models and deeper insights for both AI developers and publishers.
8.1 The Transaction Ledger
Every successful API call or self-reported event results in a verifiable transaction record. This record serves as a source of truth for billing, compliance auditing, and rights verification.
Both the AI Partner and the Publisher have access to a real-time ledger containing:
- timestamp: Exact time of access (down to the millisecond).
- path: The specific URL.
- license: License ID used for this access
- price: The exact price paid (in micros).
- identity: The user agent (and OBO developer ID, if applicable).
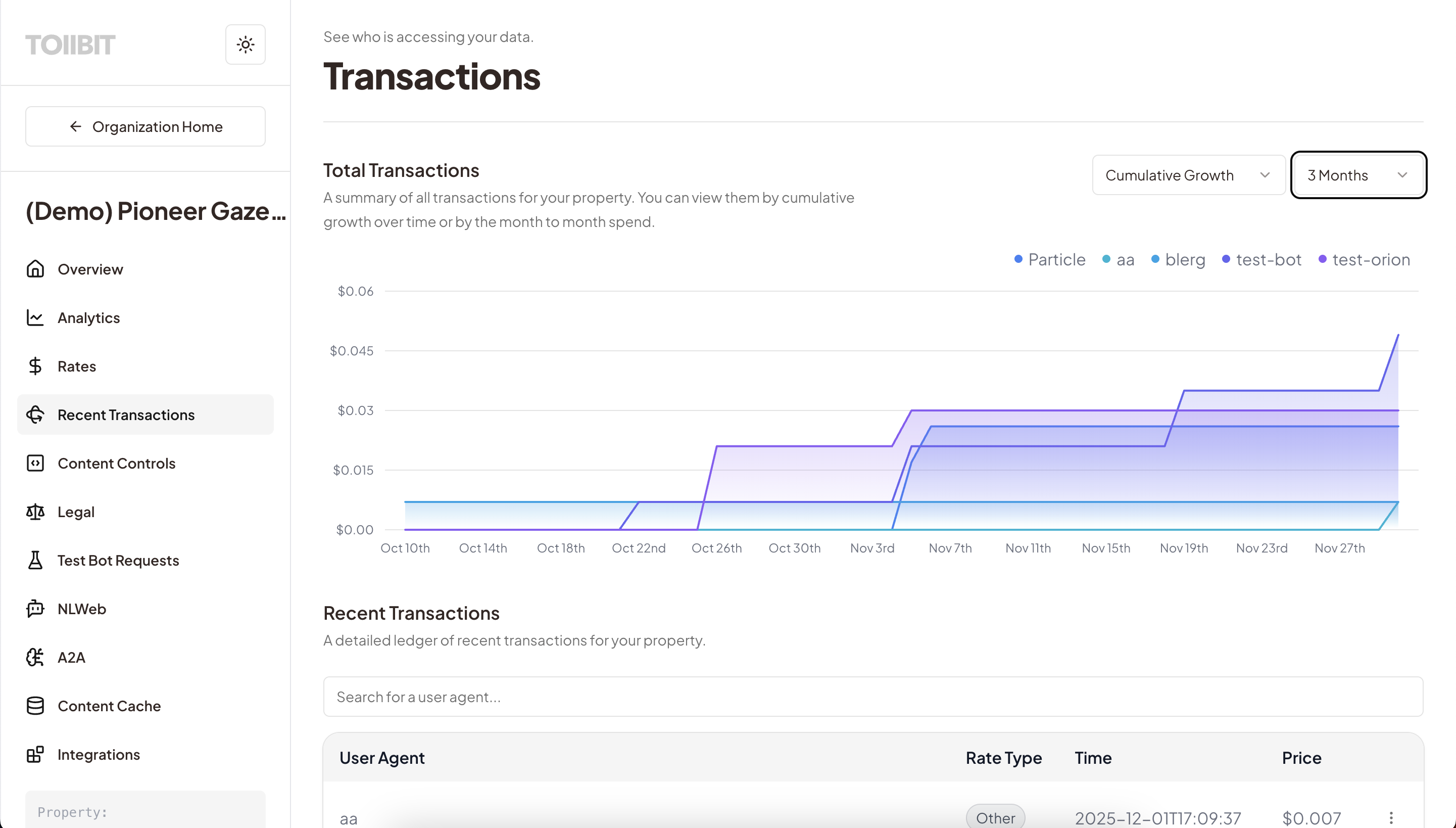
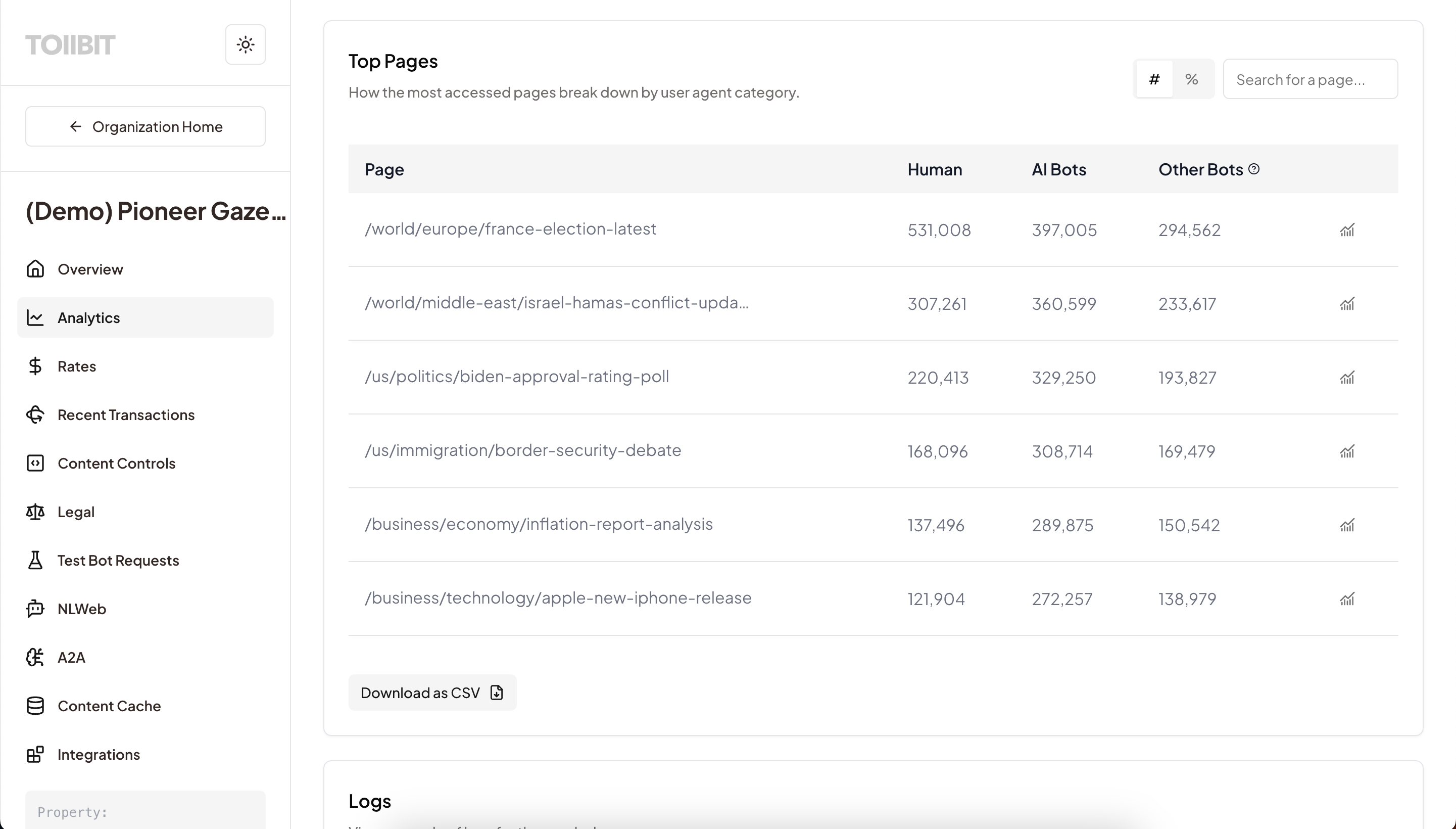
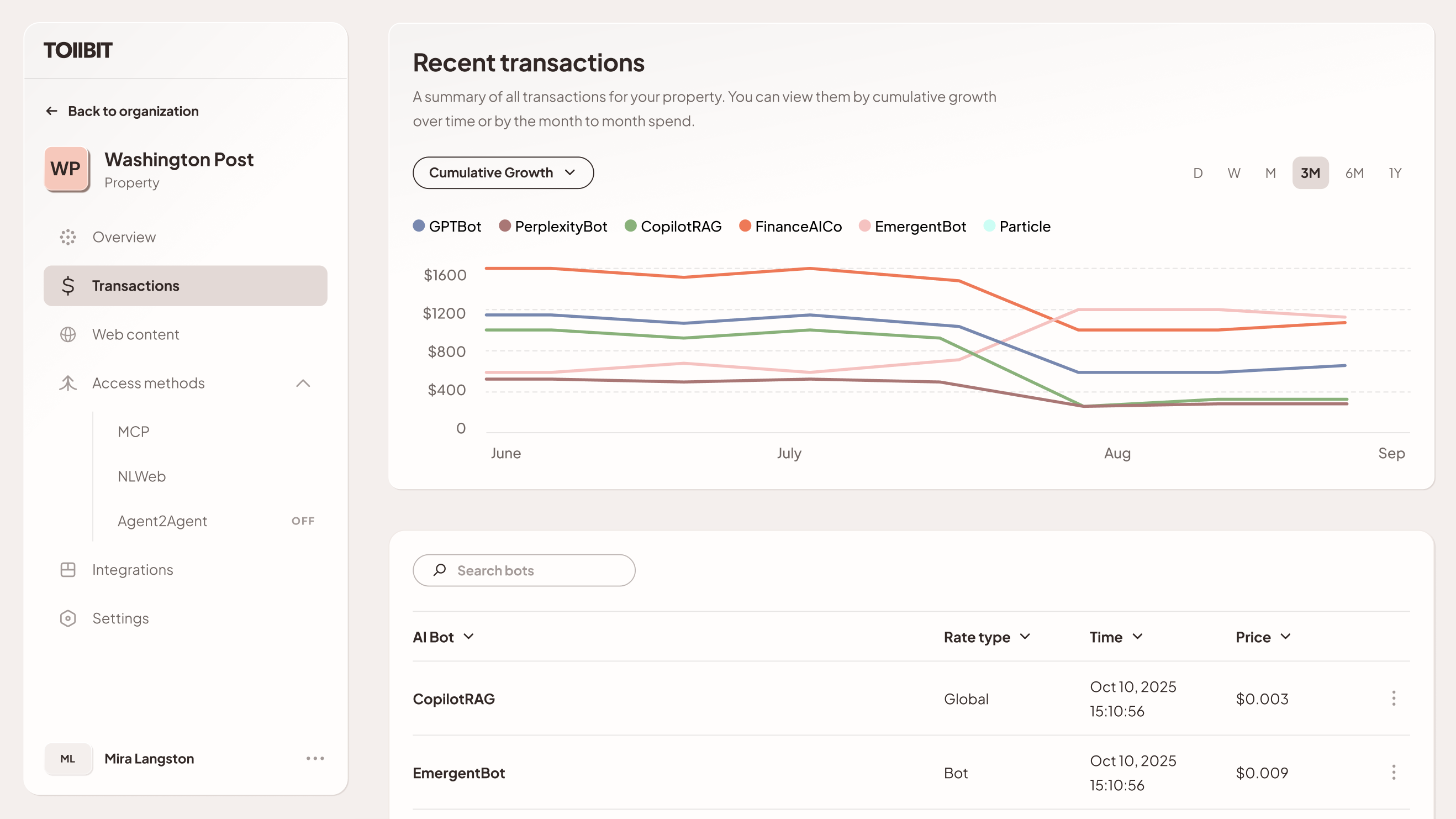
Current transaction experience above, new experience (Q1 2026) below.
8.2 Metadata Reporting
The TollBit Token and Metering API support custom metadata fields. Partners can inject arbitrary maps of data into the transaction record that may be valuable to the publisher, or required as part of a licensing deal.
Examples of metadata that may be useful:
- context_topic: "Election 2024"
- citation_count: 4
- user_intent: "price comparison"
- product_surface: "My Chat App"
This data is surfaced in TollBit Analytics, helping publishers understand why their content was chosen and informing their content strategy for the AI audience.
8.3 Referral Metrics & Click-Through Rebates
Because TollBit ingests server-side logs from all onboarded publishers, our platform has a unique view of the entire user journey - from the AI fetch for grounding to the user click-through.
This means if an AI Partner cites an article and the user clicks the link (driving human traffic to the publisher), TollBit can detect this event in our log stream.
This allows TollBit to programmatically "nullify" or discount the API charge for that specific transaction. This incentivizes developers to drive traffic, especially for high-value publishers, aligning the incentives of content creators and AI platforms.